National Gatherings

At Associa-Med, our national gatherings are the beating heart of our associationة key moments where members from all over the country come together to learn, decide, and connect. These events bring together the Local Committees (LCs) and the National Board, shaping the future of our work.
We usually hold three main gatherings each term: One National Meeting (NM) and Two General Assemblies (AGOE & AGEE)
National Meeting (NM) – October
The National Meeting (NM) is the first big gathering of the term. It’s the moment when the Local Boards and the National Board meet face-to-face to align visions and kickstart the year.
Unlike the General Assemblies (AG), the National Meeting does not include a Plenary and there are no amendments to the Internal Regulation.
The program includes:
LC Presentations
Committees Sessions (capacity-building, project planning, and knowledge sharing) & EB (Executive Board) Session
Social Program
AGOE – Ordinary Elective General Assembly (March)
This is when the National Executive Board (EB) and the Alumni Council (Conseil des Anciens – CDA) are elected.
The agenda includes:
Committees Sessions (capacity-building, project planning, and knowledge sharing) & EB (Executive Board) Session
Plenary with: Candidatures, End-of-term moral reports, Financial reports, Internal Regulation amendments, Elections for the new EB and CDA
- Social Program
AGEE – Extraordinary Elective General Assembly (September)
This is when the National Officers and Support Division Directors are elected.
The agenda includes:
Committees Sessions (capacity-building, project planning, and knowledge sharing) & EB (Executive Board) Session
Plenary with: Candidatures, End-of-term moral reports, Financial reports, Internal Regulation amendments, Elections for the remaining National Board positions
Social Program
AGE – Extraordinary General Assembly
Called when urgent changes to the Internal Regulation are needed before the next regular AG.
AGES – Statutory Extraordinary General Assembly
Held exclusively for amending the Statutes. This assembly is distinguished by the presence of a bailiff (huissier – عدل المنفذ), as required by law.
Committees Sessions
Committees Sessions are dynamic spaces where members from the same Committee come together to share experiences, build skills, and plan impactful initiatives.
These engaging training sessions cover a wide range of topics, including:
Medical Education (SCOME)
Professional and Research Exchange (SCOPE SCORE)
Public Health (SCOPH)
Human Rights and Peace (SCORP)
Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights including HIV/AIDS (SCORA)
Events Management and soft skills (internal committees)
Digital Marketing and Graphic Design (MC)
They’re designed to empower members with practical knowledge, creative skills, and the motivation to turn ideas into action.










Executive Board (EB) Session
The EB Session brings together the National Executive Board and the Local Executive Boards for strategic leadership discussions.
It is held in parallel with the Committee Sessions, giving leaders the space to focus on governance and direction while other members engage in training and project work.
Most of the time is dedicated to:
Potential Internal Regulation changes, assessing proposals and their repercussions.
Addressing ongoing challenges and finding coordinated solutions.
These discussions help ensure that every decision is well-prepared before being brought to the Plenary during a General Assembly.


LC Hour & NB Hour
After the EB Session and Committee Sessions each Local Committee delegation gathers to reflect on the sessions they attended, share takeaways, and discuss how to apply what they learned back in their local context. It’s also a space to exchange experiences between members of the same LC delegation and strengthen their teamwork. The National Board also gathers to give feedback on the sessions and discuss key points.
Plenary
The Plenary of the National General Assemblies is the highest decision-making body of Associa-Med.
Composition of the Plenary
The Presidency of the General Assembly: This body ensures the moderation of the GA. It consists of the president, the vice president of the GA, and assistants. The Chair and vice Chair of a national General Assembly of Associa-Med must be elected during the first plenary session of that same General Assembly.
CCC (Code of Conduct Committee): Responsible for enforcing the statutes and internal regulations of Associa-Med. The members of the CCC must be elected during the first plenary session of the national General Assembly of Associa-Med.
National Board Officials:
EB: President, VPI, VPE, VP-IFMSA, VPCB, Treasurer, Secretary General.
National Standing Committees Officers: NOME, NEO Out, NEO In, NORE, NPO, NORP, NORA.
Support Division Directors: MCSDD.
- Local Board Officers:
EB: President, VPI, VPE, Treasurer, Vice Treasurer, Secretary General, Vice Secretary General.
Local Standing Committees Officers: LOME, LEO Out, LEO In, LORE, LPO, LORP, LORA.
Local Internal Committees Officers: Culture, Sport, Loisirs and MC.
- Members of the Alumni Council
- Associa-Med Partners
- Associa-Med Members (LC’s Delegation)
- OC Members: (Organizing Committee) who ensure the smooth logistical running of the project.
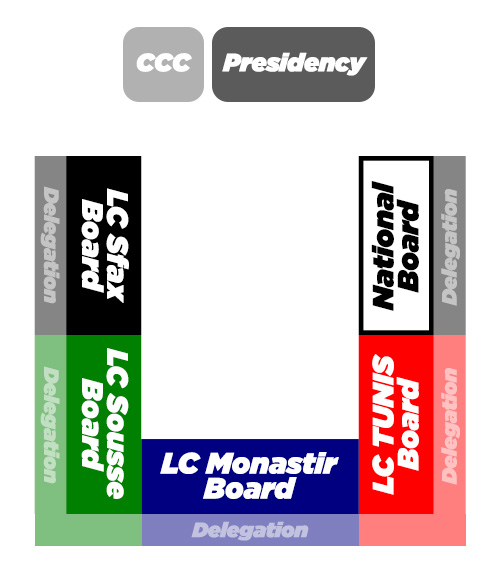
The "U" Room Setup
The arrangement of the room is strategic to facilitate debate.
The “U” Room Setup:
The National Board members are seated on the right side of the “U.”
The Local Committees are seated along the sides of the “U” in the following order: LC Tunis, LC Monastir, LC Sousse, and LC Sfax which is at the far left extremity. The voting members of each Local Committee sit in the first row, with the rest of their delegation behind them.
The Presidency and the Code of Conduct Committee (CCC) are seated in front of the “U,” overseeing the proper conduct of the plenary.

Dress Code
During the plenary, all board members must wear the official polos. The National Board wears a total black polo. For Local Committees, the polo is white with the LC’s color on the collar: red for Tunis, green for Sousse, blue for Monastir, and black for Sfax.





Quorum & Roll Call
At the beginning of each plenary session, a roll call is conducted to establish the quorum, and voting cards are distributed to each voting member. The quorum is the minimum number of voting members required for the decisions made during the General Assembly to be valid.
The quorum for an Elective National General Assembly (AGOE) on its first convocation is half of the national board officials and officials of recognized local committees.
The quorum for an Extraordinary General Assembly on its first convocation is two-thirds of the national board officials and officials of recognized local committees.
If a voting member wishes to leave the plenary, they must return their voting card to the CCC. If too many members leave, the quorum can be lost, which means that any decisions made after that point are no longer valid.





Presentations
The plenary is the moment to present and validate the organization’s official documents. Each presentation is followed by a vote for its adoption.
End of Term Moral Report of outgoing officials.
Financial Report: A summary of expenses and revenues.
National Projects Moral and Financial Report: exemple: National Social Program, national meeting …
Policy Documents: The texts that define the association’s official positions.
Small Working Group Outcomes.
National Delegations Reports: especially in IFMSA Meetings.
- . . .





Motions and Points
These are formal proposals submitted for discussion and voting. They must be sent before a period fixed by the internal regulation. They can include a wide range of actions, such as:
- Decisions regarding the session’s flow (e.g., adopting the agenda, opening or closing the General Assembly).
- Adopting official reports (end-of-term moral reports, financial reports, minutes (PV) from the last General Assembly, …)
- Changing the internal regulation.
- Adding or removing indexes.
- Opening a new small working group.
- Adopting policy documents.
- . . .
The following motions are considered procedural and can be submitted at any time during a plenary session. All procedural motions are adopted by a two-thirds majority. For these motions, the vote is opened directly; there is no need for a seconder (motion supporter) or for someone to speak against it.
Motion to adopt the agenda.
Motion to adjourn the general assembly.
Motion to postpone the debate or vote on a motion.
Motion to reopen the vote on a motion.
Motion to reopen the list of speakers.
Motion to suspend an article of the internal regulations until the end of the same general assembly or until it is resumed by the general assembly.
Motion to resume an article of the internal regulations that has been suspended.
Motion to overturn a decision of the presidence of the general assembly.
Motion to overturn a decision of the CCC.
Motion to impeach the president of the general assembly.
Motion for observers to leave the plenary hall of the national general assembly.
Motion to proceed directly to the vote.
These allow for intervention during debates and come in several types:
Points of Order: To signal a procedural irregularity.
Points of Information: To ask for or provide clear information.
Participant Rights
Right to Speak
All participants of the National General Assembly.
Right to Propose
This right allows you to formally propose a motion.
Members of the National Board, Alumni Council, Local Committees Board, GA Presidency (Chair and Vice-Chair) and CCC members.
Right to Vote and Support
Only members of the National Board and Local Committees Boards.
Majority Types
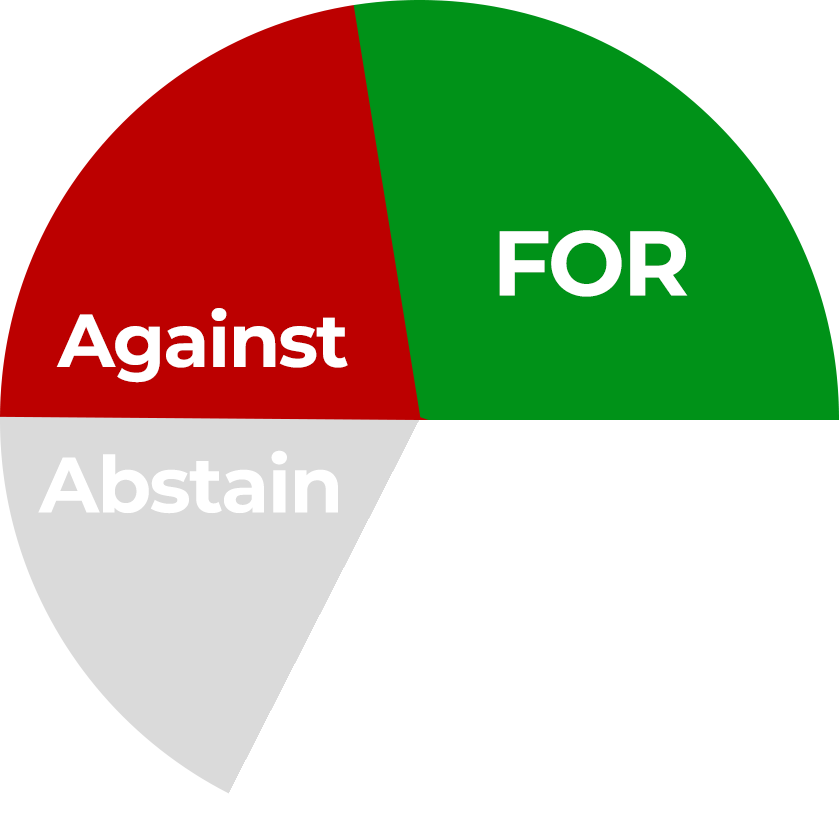
Simple Majority
The motion passes if it receives more “For” votes than “Against” votes, Abstentions doesn’t count. This is used for most decisions, including the adoption of moral and financial reports
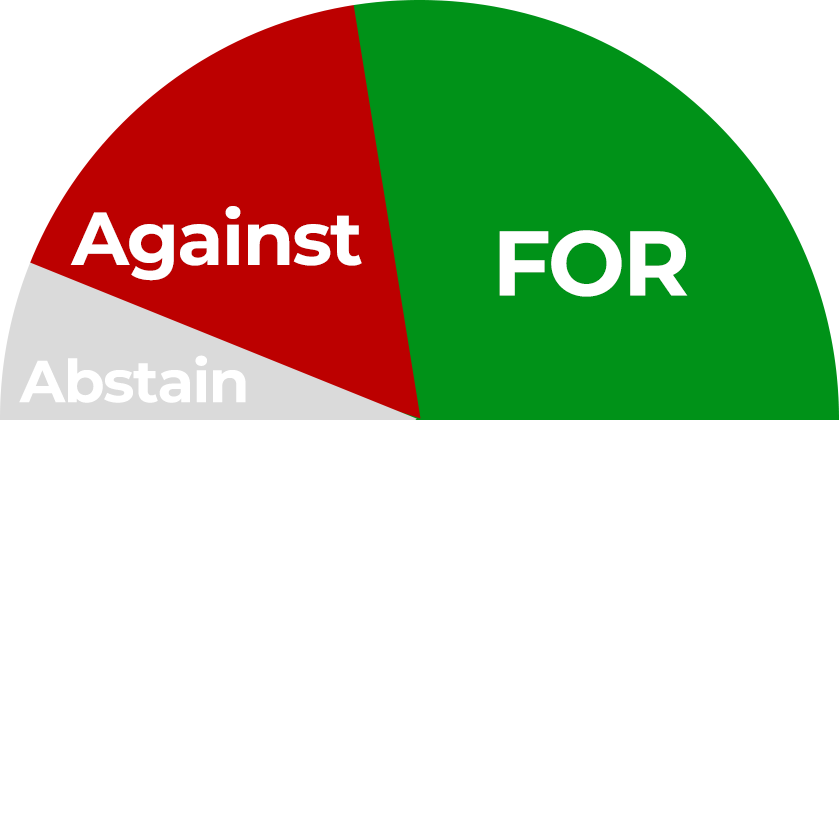
Absolute Majority
More than 50% of the total votes (including abstentions) are “For” This is used to elect a single candidate when they are running unopposed.
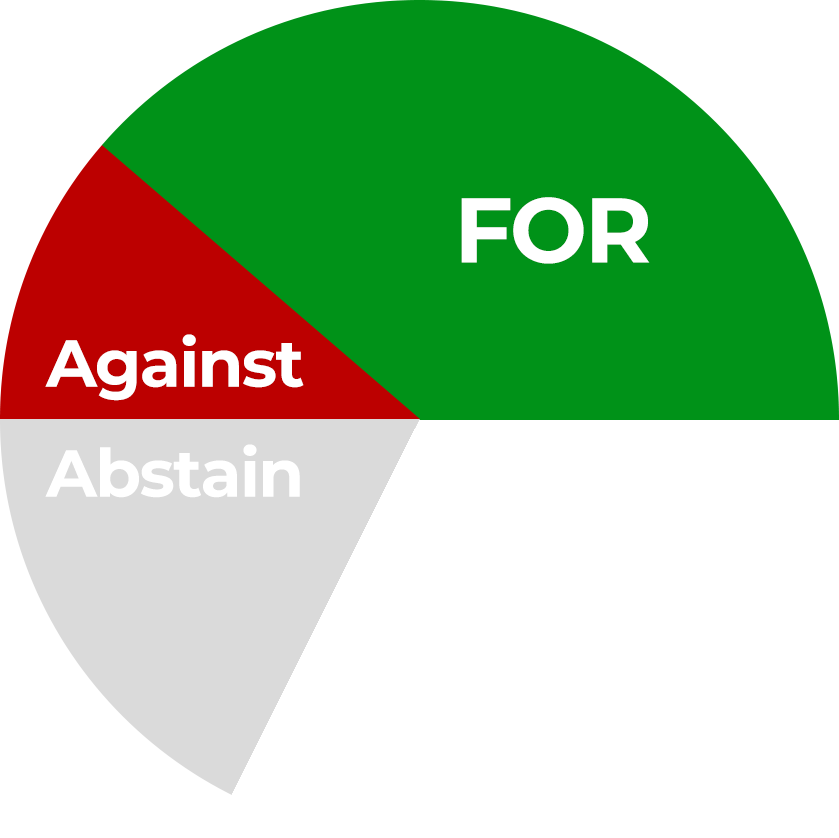
Two-Thirds Majority
The number of “For” votes must be at least double the number of “Against” votes. Abstentions do not count. This is required for: Any change to the status of Associa-Med, Changes to the “National General Assembly and Procedures” section of the internal regulations, The adoption of all procedural motions, The final closure of an investigation and Obtaining or changing the status of a local committee.
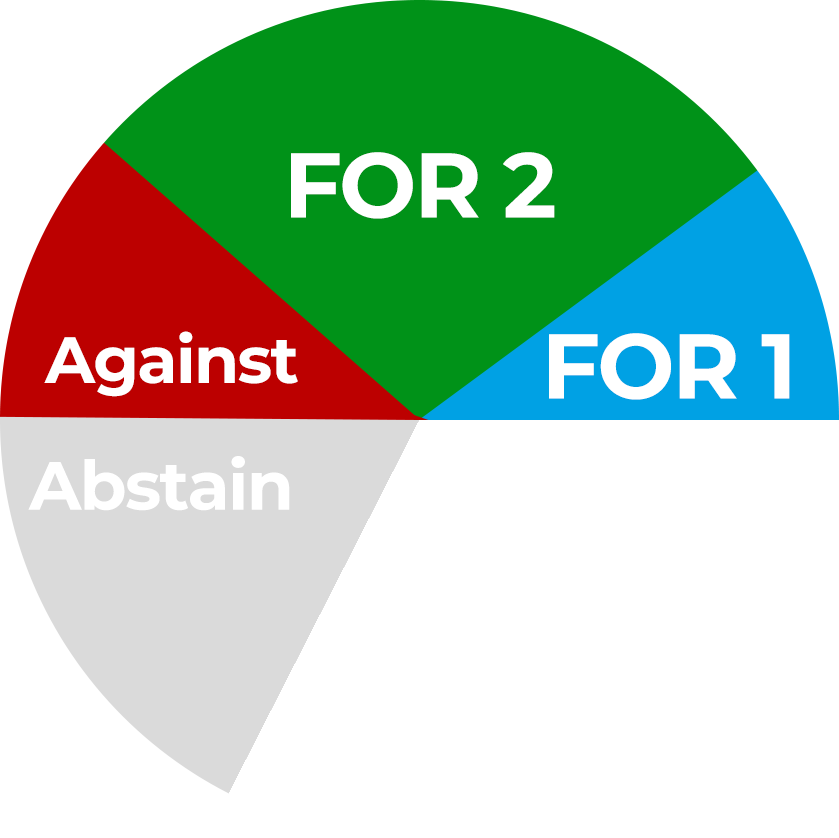
Relative Majority
The proposition that passes is the one that has the most votes. Abstentions do not count. This is used when there are multiple motions being voted on at once.
Voting Procedures
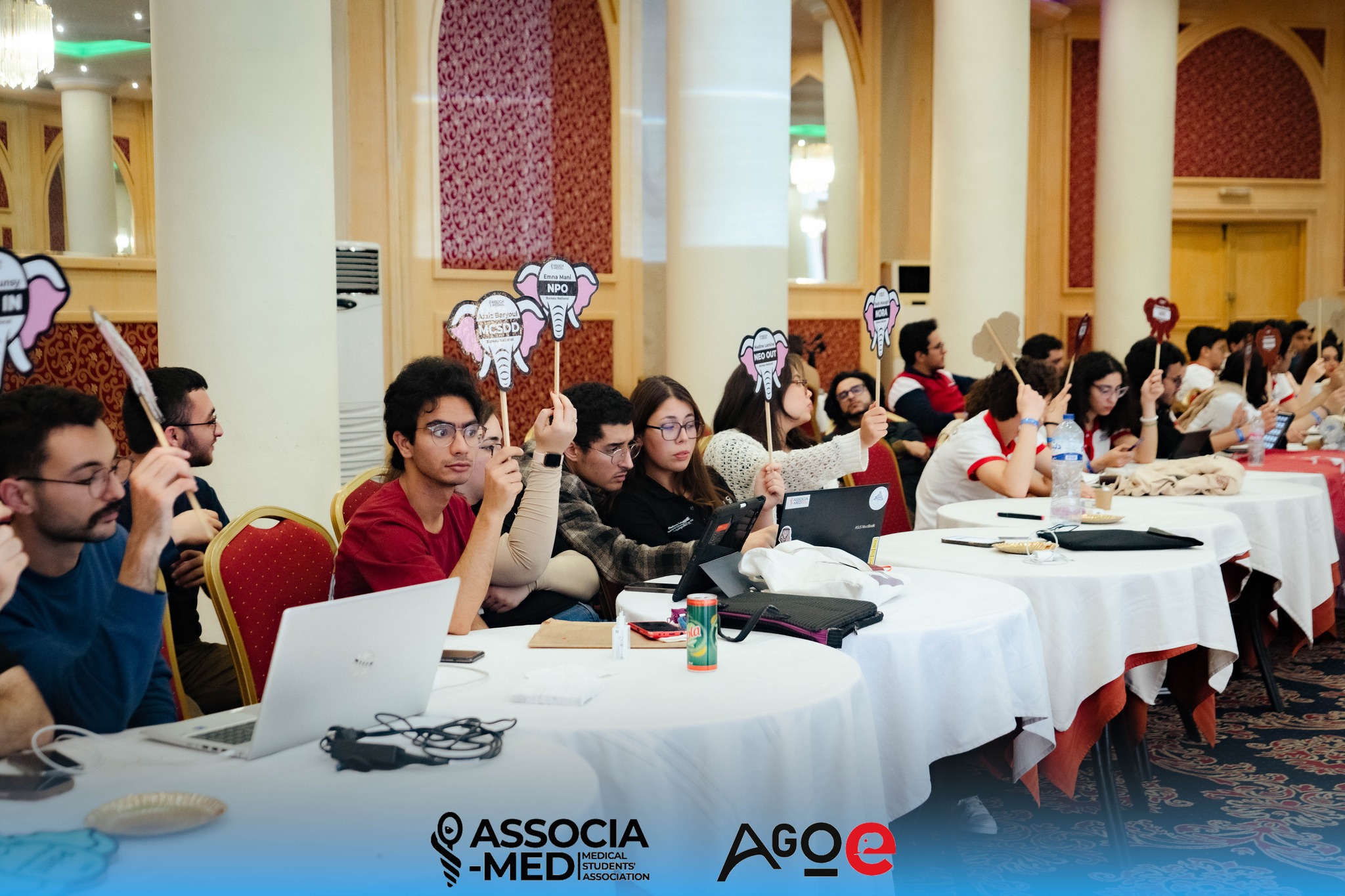
Voting Scheme: Voting procedures are clearly defined and may include a show of hands or a secret ballot. During a vote, all exits must be closed, and absolute silence is required.
Voting Methods:
- By Voting Card: When the President calls for a vote, eligible members must raise their voting cards clearly until the votes are counted. The CCC verifies that the total number of voters matches the expected number.
- By Secret Ballot: A secret ballot can be requested by any member with the right to vote. The ballot must be co-signed by the President and the National Secretary General. The Presidency is responsible for this process.
- By Electronic Voting Box: Votes can also be cast using electronic voting devices.


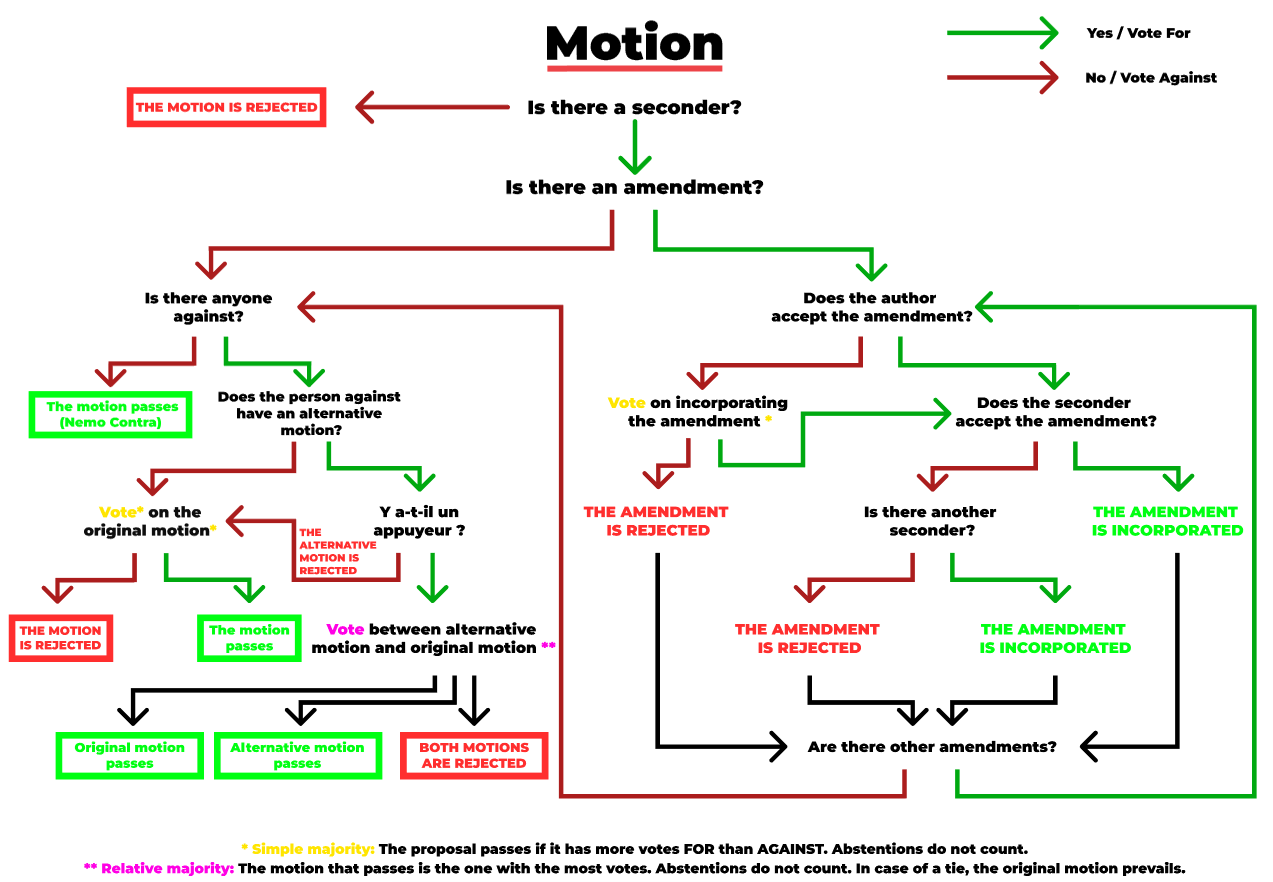
Submitting and Seconding:
Before a motion is voted on, the President must read it aloud, unless the plenary gives verbal consent. The author can briefly explain the motion’s purpose. The President then asks for a seconder. If none is found, the motion is immediately rejected.
Debate and Questions:
Any member with the right to speak can ask questions to the motion’s author. The President may open a list of speakers, with the author having the right to speak last.
Withdrawal:
A CCC-accepted motion cannot be withdrawn before a vote without the consent of both the author and seconder. If the author withdraws before finding a seconder, the motion is withdrawn. If the author withdraws after a seconder is found, the seconder becomes the new author, and a new seconder must be found. Once the debate is closed and the vote is announced, the motion cannot be withdrawn.
Amendments:
After the debate closes and the vote is announced, the President will ask for proposed amendments. Only those with the right to propose can submit an amendment.
Author/Seconder Approval: The President will ask the original author if they accept the amendment. If they do, the seconder is asked for their approval. If both agree, the amendment is immediately incorporated. If the author accepts but the seconder does not, another seconder must be found. If none is found, the amendment is rejected.
Vote on Amendment: If the original author does not accept the amendment, a vote is held to include it. The amendment requires a simple majority to be included in the original motion.
Debate on Amended Motion: The President can open a new speakers’ list to debate the amended motion.
Unanimous Adoption:
If, after all amendments are handled, no one is against the motion, it is adopted unanimously.
Alternative Motions:
Only members with the right to vote can be against a motion. If a member is against it, the President asks if they have an alternative motion. If no alternative is proposed, the vote proceeds directly. If an alternative is proposed, a seconder must be found. If an alternative is seconded, both the original and alternative motions are voted on.
Motion Adoption:
A motion is adopted if:
No member is against it.
It obtains a simple majority of votes.
It obtains a relative majority of votes when an alternative motion is proposed. In case of a tie, the original motion is adopted.
Reconsideration:
A rejected or adopted motion cannot be reconsidered unless the procedural motion “Reopen the vote on a motion” is adopted.
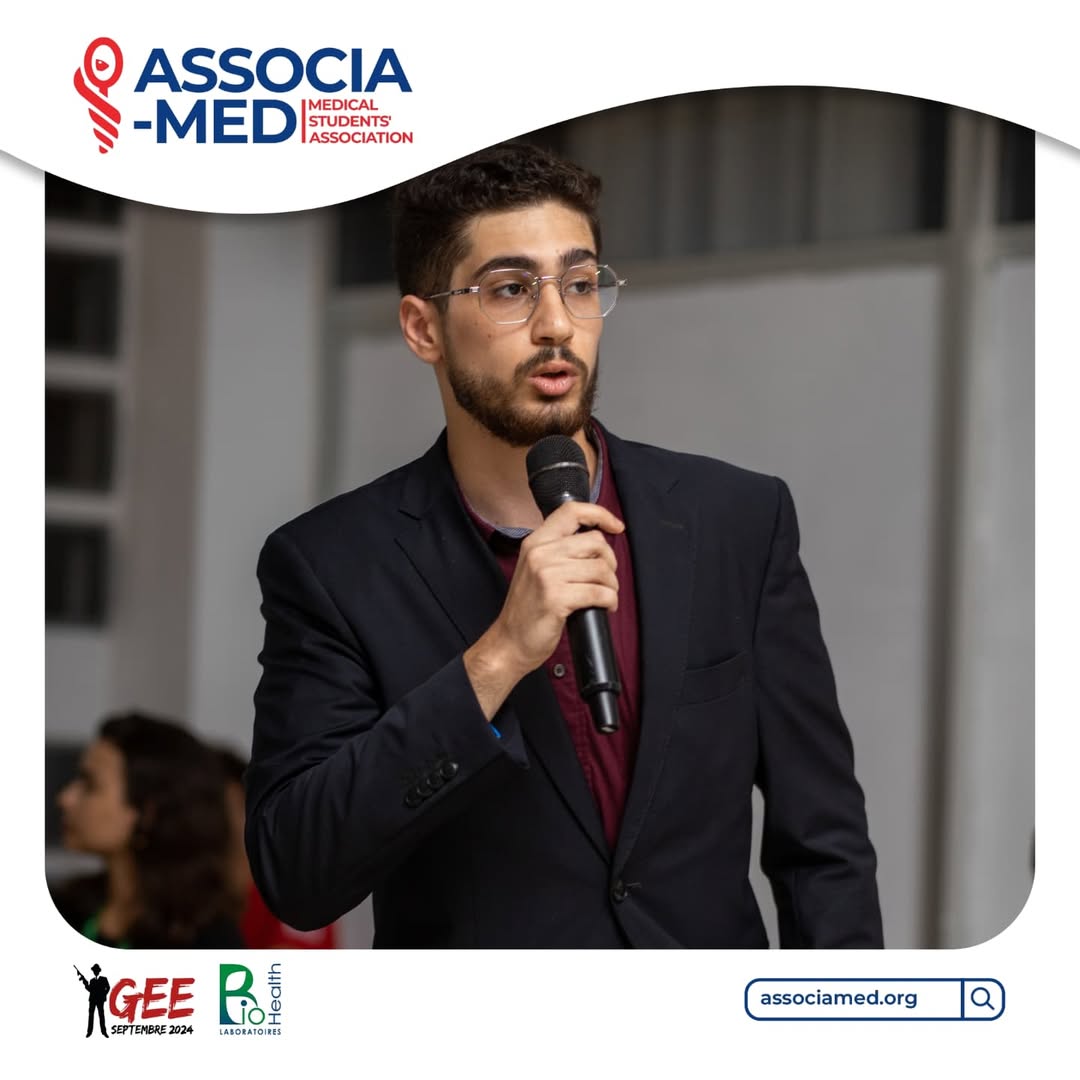
Candidacies
During the plenary session, candidates for leadership positions present their vision, mission, and plan of action. After their presentation, any person with the right to speak may ask them questions.
Sometimes, a “Candidate Debate” is held in an anonymous format, with questions submitted and answered at a dedicated time outside of the plenary session.
Additionally, candidates may go to different “LC hours” to present and explain their plans in a less official way and answer questions.




Elections
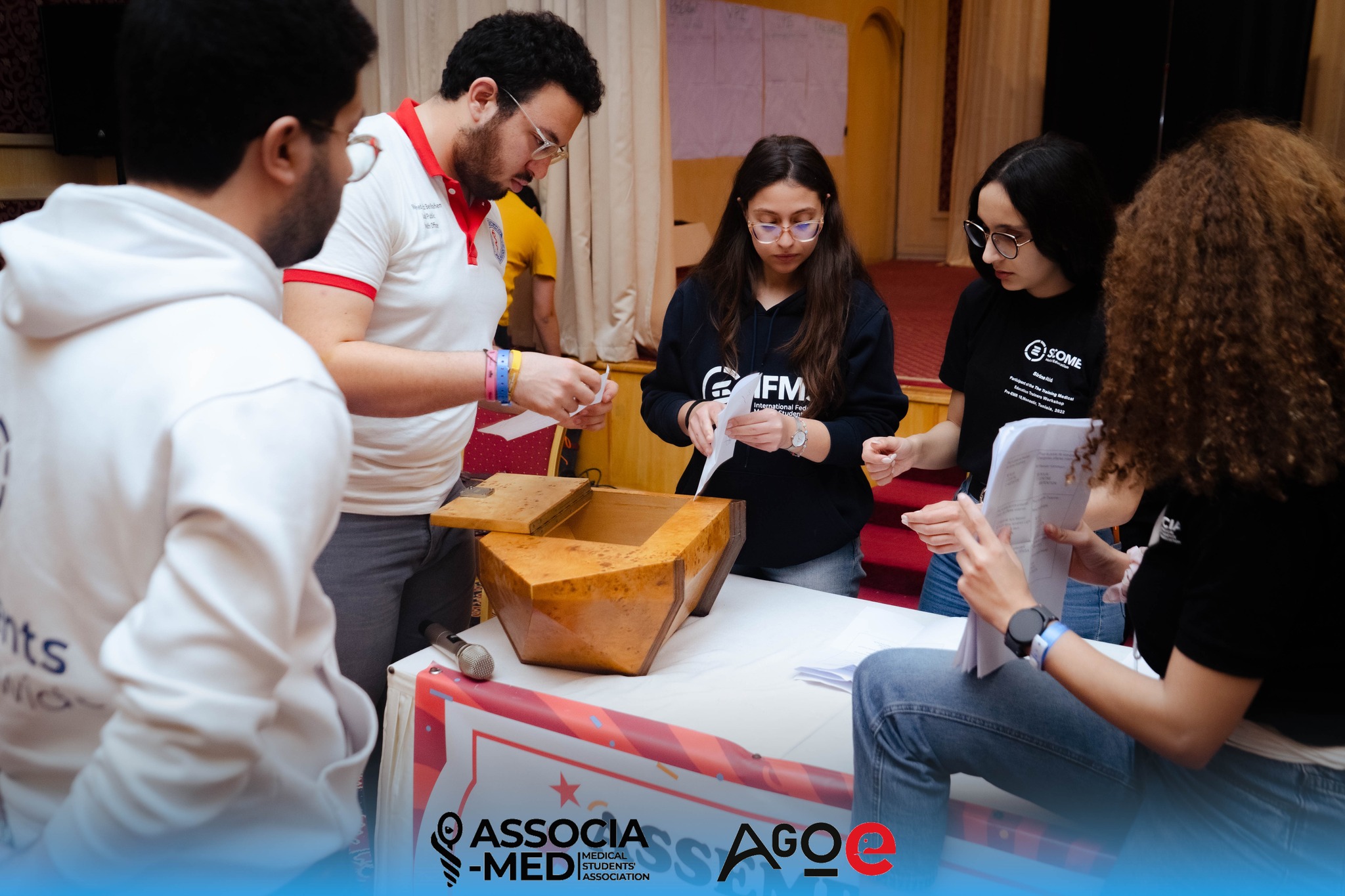
The final vote takes place during the last plenary session via secret ballot to ensure anonymity and fairness, and the count is performed transparently.
If one candidate runs: They must get an absolute majority of the votes to be elected.
If two candidates run: The one with the relative majority wins, provided the total votes for both candidates reach an absolute majority. Otherwise, both are eliminated.
If more than two candidates run: The election is by relative majority, provided the total votes for all candidates reaches an absolute majority. If no candidate gets an absolute majority in the first round, the two candidates with the most votes proceed to a second round.


The Social Program
The social program is an essential and highly anticipated part of the National General Assembly. It is designed as a space for pure fun, dancing, and celebration, offering a complete break from the formal sessions and debates of the day. Taking place at night after the official plenary sessions and a shared dinner, this is when the atmosphere transforms from one of rigorous governance to one of genuine camaraderie and jubilation. The focus is entirely on allowing participants to unwind, connect with old friends, and form new bonds in a relaxed and energetic environment.
























